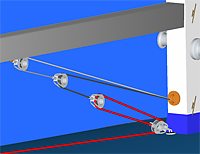
I didn't know if I should call this "Splicing Samson Untra-lite", "Integrated Soft Shackle Light Air Sheet", "Soft Light Air Sheet", or "The Ultimate Sheet for Light Air Sailing". Maybe "How I Went From Doing Pirouettes in Light Air to Nirvana." The truth is that it is all of these.
In most of the time I owned Papoose, if the wind got below 5 knots the boat would just sit there and turn usually backing to the wind. Now I have a free flying light air jib, a spinnaker and thses sheets, sailing in 5 knots of wind is my favorite sailing condition.
View Article
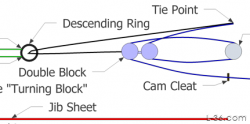
Y-Sheet use for spinnakers is not a new idea. In fact, it is widely used but typically requires tying to the clew with a bowline. That makes using high tech lines like Amsteel problematic because knots slip in Dyneema. In this implementation, the attachment to the clew is just like a soft shackle but unlike a traditional soft shackle, the shackle is divided into its key elements with the adjustable eye integrated in the Y-Sheet itself and the diamond knot permanently attached to the clew ring.
View Article
Splice of 1/8 inch Amsteel-Blue to 1/4 inch Sta-Set is shown. This is ideal for the halyard of a small boat and is also a scale model for a 3/16 Amsteel to 3/8 Sta-Set splice, which would be good for a 36 foot boat. I have tested this splice to the breaking strength of the StaSet and the splice holds fine.
View Article
This is the first part of a two part tutorial on mechanical systems made from blocks and line. The second part is
HERE. I will explore the mechanical advantage of various systems, and shows the general principles on how to set these systems up, including how to thread the line through the blocks, or reeve them. It will go from 1:1 to 6:1 with simple systems and up to 24:1 with cascaded systems. The second part will explore some more unusual systems.
View Article
Have you ever wondered hom much, if anything, you are giving up by using fairleads instead of blocks? How much friction is there. How does this compare with a block? Does the style of the fairlead matter? This article attempts to answer these questions.
View Article
Yet another way to make a soft halyard shackle out of Amsteel. This is one that I am using on my boat. The advantage is that the hybrid knot gives approximately full line strength but only extends a couple of inches so that the short splice will not end up making the line that goes into the sheaves fatter. This prevents extra wear in thinner halyard sheaves. The knot provides the locking action which removes most of the load from the splice.
View Article
An inhauler, sometimes called a Barberhauler, is used to pull the jib sheets inboard from their normal position. You can do that to decrease the sheeting angle or to keep the sheeting angle the same as you let the sheets out to add fullness.
View Article
A Jibsheet Twing is sometimes called a Jib Sheet Downhaul. It is used instead of moving the jib car when you sail off the wind. At least that is what I do and it is so much easier than trying to move the car even if you have lines to move the car. This article also discusses sail trim for off the wind and how a twing can help get good trim.
View Article
Do you find that you get wraps on your jib winches or just want give a better lead angle to the winch? In the last race we did, a new crew member got a wrap so tight that the only way to release it was to cut the sheet with a knife. We strung the lazy sheet to the secondary winch and took the pressure off but that was not enough to free the wrap, that is when the knife came out. The winch manufacturer recommends between 3 and 8 degrees as the ideal sheeting angle.
View Article
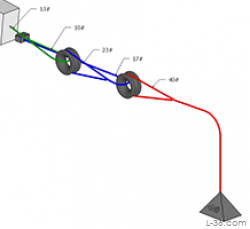
I recently saw a picture of a three stage cascaded block system using low friction ring instead of blocks. This article analyzes such a cascade and shows how to calculate its effective mechanical advantage. The techniques shown can easily be extended to other systems. I will discuss one such system that I use on my boat.
View Article
For about $75 I have a 100 ft long light weight easy on the hands halyard to replace the wire main halyard. The trick is the choice of cover material and the splice while keeping the strength thought the entire length.
View Article
It isn't often you see a completely new way to rig a mainsheet. I saw this posting on Sailing Anarchy and though I would share an analysis of what they are doing and why. Here is a picture of the boat
View Article
Papoose has a Double Ended 5:1 Mainsheet System. I explain it as well as show most other popular mainsheet systems in this mainsheet systems page.
View Article
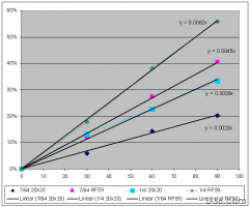
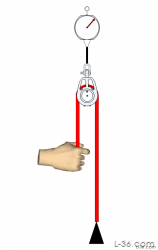
In the first article of this series we gave results on using fairleads and showed how the added friction is not significant with low deflection angles. In this article we consider using low friction and other standard rings with high deflections and analyze how these can be used in systems to provide simple and inexpensive mechanical advantage. Again we used the digital scale shown on the right to make the measurements. This scale reads up to 220 pounds with 1/2 pound resolution.
View Article
I have several articles on using rings as inhaulers and twings. This can be taken to extremes and the jib car can be eliminated and just the twing and inhauler used. It not only can be, that is how the TP-52 fleet is rigged. Here are some pictures to show it. This is a picture I took a couple of years ago at the Big Boat Series in San Francisco of the TP-52 Mayham
View Article
A simple and easy to use method of attaching a halyard to the head of a mainsail is shown. There are no parts to drop or complicated things to do. The toggle is permanently attached to the halyard and a simple trick makes it all work.
View Article
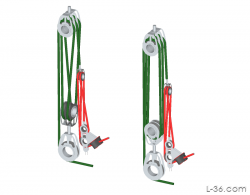
A 8:1 Vang system that is cheaper than using two fiddle blocks, lighter, and stronger. What is not to like?
The second vang system shows is the 20:1 vang on Papoose. This is a unique system with some advantages that are discussed.
This page also has a link to 16 standard variations on vang systems.
View Article
Hybrid Soft Halyard Shackle

Yet another way to make a soft halyard shackle out of Amsteel. This is one that I am using on my boat. The advantage is that the hybrid knot gives approximately full line strength but only extends a couple of inches so that the short splice will not end up making the line that goes into the sheaves fatter. This prevents extra wear in thinner halyard sheaves. The knot provides the locking action which removes most of the load from the splice. The short bury distributes the load enough so that not all of the load in on the knot. The result has been tested to near full line strength. This knot is one of just a few that do not slip in Amsteel. The knot is strong and the splice prevents slippage.
View Article
8:1 and 20:1 Cascade Vang Systems (and link to 16 more vang systems)
A 8:1 Vang system that is cheaper than using two fiddle blocks, lighter, and stronger. What is not to like? You just run the control line back to the cockpit where you put a cam cleat. You will likely need a turning block on deck but then you have the vang where you want it when it needs to be released quickly before you round up.
The second vang system shown is the 20:1 vang on Papoose. This is a unique system with some advantages that are discussed.
This page also has a link to 16 standard variations on vang systems.
View Article
The First Bend

This bend has been tested. Sometimes it slips, sometimes it breaks. Either way it is stronger than a triple fisherman's. Amsteel is very slippery. It is difficult to test a knot that slips and even harder when it slips sometimes. If you pull and let it sit after it starts to slip, it recovers and ends up being strong, something above 40% of line strength by some tests. There are other knots that almost never slip, see the Last Bend but it is ugly and not near as simple or easy to tie as this knot. The standard for tying Amsteel or Dyneema together is the triple fisherman's knot. This knot slips less that a triple fisherman's so it is a step forward slipping or not. When it doesn't slip, it is stronger than the Last Bend. I present it here for your consideration.
Both the First Knot and the Last Bend can slip at about 35% of line strength. When they don't slip, they are about 40% of line strength with the First Knot just a little above this and the Last Bend below this. There is another variation that slips at about 40% that I will show here as well. You can untie the First Knot, but not the variation.
This knot can also be untied even after being loaded up near breaking. Just put a spike through the center to loosen it up and remove the tails from the knot center. The rest is easy.
I am calling this knot the First Bend because by the time I was done testing dozens of variations on knots and never wanted to hear the word bend again, I called the final knot the Last Bend. It did well but upon considering this knot, the first one I considered, I came to appreciate it more. In fact, I am declaring it the winner of my search for the best bend for Dyneema. That said, the variation is stronger.
View Article
High Strength Soft Shackle
Recient work by Brion Toss, Evans Starzinger, and myself has led to the development of a high strength soft shackle that Evens has tested to 230% of line strength. The secret to this added strength in primarily an increase in the strength of the knot, the weak point in conventional soft shackles. I should point out that Evans testing shows conventional soft shackles, with diamond knots, test at 170% of line strength, considerable above the "higher than line strength" number I have been using. While these two statements are consistant, the more percise number is considerably higher and higher than the testing I had done at NE Rope.
View Article
Main Halyard Soft Shackle Variation
This soft shackle in integral to the main halyard. It is made from a single line with a combination of knots with a finishing splice. I have tested it to over 1000 pounds using 3/16 Amsteel without slip. While I have not tested it to destruction it is very likely that the shackle is stronger than the line so that the failure would be outside of the shackle area. I base that on the fact that the shackle area is made of either 2 or 4 lines so any loss due to the knots is unlikely to bring the strength below line strength. Of course, a halyard is typically not loaded that high as the application is mainly stretch limited. That said, be sure to do your own testing before using this in any critical application.
|
View Article
Gross Fine Mainblock Reeving
Two ways of reeving the mainsheet in this gross fine mainsheet system are shown. The more obvious way to do it is shown on the right. The problem is that the lines hit each other, the fine control blocks hit the main sheet, and in general it has problems.
The other way rotates the main dual block by 90 degrees and has no such interference issues. It also opens up a large space for the fine tackle so that it does not rub on the mainsheet.
View Article
Soft Halyard or Line Shackle

I am calling this a soft halyard or line shackle as it is certainly not confined to use only on halyards. It is a combined splice-shackle and is similar to a soft shackle where the opening eye is on the line and the knot is on a second piece. It is much faster to use than a soft shackle. In applications where the line is 12 strand spectra such as Amsteel, this is a perfect fit. I have tested it to destruction and the failure was similar to other tests of soft shackles which broke at the diamond knot. Based on all these tests, my conclusion is that it is 80-90% as strong as the line. I must add, the force I put on my 1/8 inch Amsteel using a hydraulic jack was huge, many times the force I got using a Barient 22 winch even with 1/8 inch line. In other words, this is a strong, easy to use shackle is integrated into a line such as a halyard. The line in all these photographs is 3/16 Amsteel Blue.
View Article
Soft Line Shackle on a Block
Using a line shackle and stopper loop you can in some cases eliminate hard shackles even from places that would be impossible to do with normal soft shackles. The stopper loop can be "tied" to the clevis pin and the soft shackle integrated into the line for a clean light installation.
View Article
Double Soft Shackle
This double ended soft shackle is the 4th generation of a design that can attach to a pair of eye spliced jib sheets to the clew of a sail very quickly. It is also the 5th version of this generation as improvements were made to make the shackle stronger. In use, the shackle is secure around the jib sheet prior to being "clipped" to the clew. This version is easy to make and has the advantage of a non-constricting hold on the jib sheets. There are links to the previous versions at the bottom of this page
The Shackle

View Article
A Better Soft Shackle
My "Better Soft Shackle" has become the standard in soft shackle design along with the
stronger soft shackle. I invented this version several yeas ago and was co inventor of the stronger soft shackle along with the late Brion Toss and Evans Starzinger. Of the two versions, I prefer this one. It is easier to tie and easier to use. If I want a stronger shackle, I start with stronger line. For example, the stronger soft shackle is 35% stronger but going up one line size gains 60% in strength. All things considered, I believe this is the superior version.
The original soft shackle is rather difficult to open and to milk closed. With age, it becomes increasingly difficult. The alternative Kohlhoff style is easy to use, but it sacrifices some security. This version incorporates the best properties of both of these versions. The eye is easy to open but can only be opened just enough to fit the stopper knot through it. Almost any slight force will close it quickly.

View Article
Soft Shackles
This is the introduction to a series of 6 pages that deal with soft shackles. Step by Step instructions on
How to make a soft shackle, some
Variations, and some detail on the
diamond stopper knot, . . These are incredibly strong. I show
how they are used, below. Nothing is useful until it has been
tested , so check that page out. There is even a
Calculator so you can make them come out the length you want. Enjoy the series.
To the left is a picture of the soft shackle on the jib clew. The addition of the Velcro keeps the diamond knot in the center of the clew ring where it will stay out of the way of the rigging. These shackles are very strong. I did some testing and it is clear that the sheet with the eye and the soft shackle is much stronger than the sheet with the bowline. In my testing, the line broke at the bowline. You can follow the links above and see how to make them, as well as the testing that I did. I did the testing at 2/3 scale which is a little less than 1/2 the strength. The test at the bottom of the page was done to distruction of a link line made of the same Amsteel thus showing that a soft shackle is stronger than the line it is made from. On the rest of this page, I show how to use a soft shackle.
View Article
Soft Shackle Spinnaker Y-Sheet
My old friend the dual soft shackle version 1 has found a new use. It is common practice to use some kind of tail on an asymmetric spinnaker to keep the clew away from the rigging. One version is called a Y-Sheet. It connects to eye splices in the sheets and extends to some kind of connection to the clew either with a knot or a shackle. This article shows how to use a soft shackle type arrangement and not only avoid the strength loss that you would get with a knot, but basically doubles the strength of the line used for a penalty of a small increase in the length of the rope you need.
View Article
There are lots of ways to tie a bowline. I think this is the quickest, fastest, easiest to do and remember of all the ways. I learned this when I was a kid from my dad. He probably learned it in the navy in WW II, not sure. But I do know he was a sailor and knew how to tie a bowline fast.
View Article
NOTICE: Some pages have affiliate links to Amazon. As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
Please read website Cookie, Privacy, and Disclamers by clicking
. For my YouTube page click









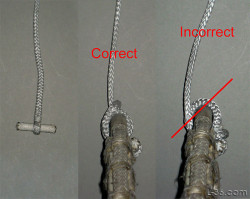
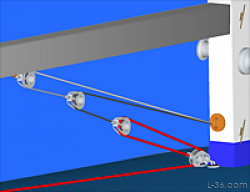
 Yet another way to make a soft halyard shackle out of Amsteel. This is one that I am using on my boat. The advantage is that the hybrid knot gives approximately full line strength but only extends a couple of inches so that the short splice will not end up making the line that goes into the sheaves fatter. This prevents extra wear in thinner halyard sheaves. The knot provides the locking action which removes most of the load from the splice. The short bury distributes the load enough so that not all of the load in on the knot. The result has been tested to near full line strength. This knot is one of just a few that do not slip in Amsteel. The knot is strong and the splice prevents slippage.
Yet another way to make a soft halyard shackle out of Amsteel. This is one that I am using on my boat. The advantage is that the hybrid knot gives approximately full line strength but only extends a couple of inches so that the short splice will not end up making the line that goes into the sheaves fatter. This prevents extra wear in thinner halyard sheaves. The knot provides the locking action which removes most of the load from the splice. The short bury distributes the load enough so that not all of the load in on the knot. The result has been tested to near full line strength. This knot is one of just a few that do not slip in Amsteel. The knot is strong and the splice prevents slippage.